Уолл-стрит: почему Intel разделил Mobileye и публично пойти? Проблемы из китайских аналогов являются жестокими
Dec 17,2021
Несколько дней назад Corporation Intel объявила, что планирует продвижение листинга Mobileye в Соединенных Штатах в середине 2022 года через первоначальное общественное предложение (IPO). Каковы основные причины за этим? В связи с этим Роберт Кастеллано, старший аналитик на Seekingalpha, анализ анализа рынка фондового рынка Уолл-стрит, сделал анализ.

Mobileye в настоящее время предоставляет современные системы помощи драйвера (ADAS) и соответствующие продукты более чем на 30 автопроизводителей, которые выбрали Edque в качестве их вспомогательных технологий вождения. Эти автопроизводители включают Audi, BMW, Fiat Chrysler, General Motors, Honda и Hyundai. , Kia, Nissan и Volkswagen.
Согласно данным Intel, ежегодный доход Summerye в 2020 году составил 967 млн. Долларов США, а в 2019 году было 879 миллионов долларов США, увеличившись на 10% в годовом исчислении. Компания рассчитывает достичь рекордных годовых доходов в этом году, что, как ожидается, будет более чем на 40% выше 2020 года. В 2020 году до 2020 года поставки CHAMET CHAMET CHADQ составили 19,3 миллиона по сравнению с 2,7 миллионами в 2014 году, представляя собой составную годовую скорость роста 39 %
В то время как Mobileye привлекла многие клиенты, Qualcomm объявила о своем сотрудничестве с BMW на 2021 инвесторовской конференции. Новые автомобили BMW будут использовать Snapdragon Snapdragon Snapdragon Snapdragon (включая чипсы) от 2025.
В дополнение к разрыву производительности обсуждается позже в этой статье, чип Intel's 3940 относится к серии E3900, которая была выпущена в 2016 году, используя процесс 14nm. Сначала он был в основном использован для чипов потребительских классов, а затем он был отдельно классифицирован как чипсы автомобильных классов. Компания CAR-класса - это серия A3900, а стоимость составляет около 40 долларов США. S8155 Qualcomm MakeComm - это высококачественный микросхемы, который стоит около 100 долларов.
Большинство самостоятельно-транспортных средств используют системы с камерами, радарами, лазерными датчиками и другими техническими системами для оценки дорожных условий и корректировки поведения вождения. Эти автомобили могут иметь адаптивный круиз-контроль, регулировку полосы движения полос и автоматическое торможение, рулевое управление и системы ускорения.
Уровень автономного вождения неотделимо от вычислительной мощности чипа. Автономная водительская промышленность, как правило, считает, что мощность вычислительной мощности чипа, необходимая для уровня 2 (триллион операций в секунду, «топы»), составляет менее 10 верхов, уровень 3 требует от 30 до 60 топов, а уровень 4 требует 100. Топы или выше, уровень 5 требует 1000 топов или выше. Именно из-за этого, что чип вычислительная мощность стала основной силой конкуренции между различными чипами.
Если автомобильная компания использует несколько чипов для настройки контроллера автономного вождения, они могут достигать 1024 топов, которые могут поддерживать автономное вождение уровня 4.
Хотя вычисляющие топы мощности одного чипа является ключевым индикатором, это не единственный индикатор. Автономное вождение - сложная система, которая требует совместной работы облака автомобильного дороги. Следовательно, в конкурсе чипов автопилота, в дополнение к ядру, существует также сотрудничество программного и аппаратного обеспечения, а также платформа и цепочка инструментов.
В настоящее время на автомобильном рынке Chip Ai Compints, которые негативно затронули Intel и Mobileye, включая Qualcomm и NVIDIA, TESLA и китайскую компанию Huawei, Horizon, Black Seaname и Technology Chi Chi.
Seekingalpha также перечислена подробная информация о продуктах и планах конкурентов Mobileye.
Qualcomm
Серия Intel A3900 основана на дизайне архитектуры x86 и была выпущена в 2016 году, используя процесс 14nm. Сначала он был в основном использован для чипов потребительских классов, а затем он был отдельно классифицирован как чипсы автомобильных классов. Компания CAR-класса - это серия A3900, а стоимость составляет около 40 долларов США. Обновленная версия EyeQ4, EyeQ5, будет выпущена в 2020 году. EyeQ5 был установлен только на модели Geely 001 Geely 001 в течение первого четвертого квартала этого года. EyeQ5 принимает 7nm Finfet Process, CHIP вычисление мощности составляет 24 верхних вершины.
SA8155P - это интегрированная платформа Cakpit встроенная кабина следующего поколения. Это чип уровня системы 7nM, разработанный с пользовательскими аппаратными модулями, включая восьмидерную подсистему CPU, и принимает CPU Qury Chare CROO, на основе архитектуры ARMV8. Чип уровня системы использует эффективную архитектуру машины, потребляемая мощность составляет менее 7 Вт, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 10 топов.
Платформа Snapdragon Snapdragon Qualcomm MakeComm MatoComm SA8295P использует 5 нм технологию технологии, с пропускной способностью чипов до 30 топов.
SA8155P - это интегрированная платформа Cakpit встроенная кабина следующего поколения. Это чип уровня системы 7nM, разработанный с пользовательскими аппаратными модулями, включая восьмидерную подсистему CPU, и принимает CPU Qury Chare CROO, на основе архитектуры ARMV8. Чип уровня системы использует эффективную архитектуру машины, потребляемая мощность составляет менее 7 Вт, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 10 топов. Платформа Snapdragon Snapdragon Qualcomm MakeComm MatoComm SA8295P использует 5 нм технологию технологии, с пропускной способностью чипов до 30 топов.
NVIDIA
Процессор Xavier имеет программируемый ускоритель CPU, GPU и глубокого обучения, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 30 топов. NVIDIA's Next-Generation Autopilot Chip Chip Chip также начнет массовое производство в 2022 году. Одной вычислительной мощности чипа Orin составляет 254 топов, что в 10 раз выше, чем вычислительная мощность EyeQ5. Вычислительная мощность NVIDIA ATLAN на вычислительной емкости NVIDIA может достигать 1000 топов (ожидается, что оно обеспечивает образцы разработчикам в 2023 году).
Huawei
Huawei позиционирует его как поставщик уровня 1 и построить «автомобильную экосистему 5G» с целью высококачественного автономного рынка вождения, который нельзя игнорировать.
Вычислительная мощность чипа Huawei Ascend 310 может достигать 16 топов, а потребляемая мощность составляет всего 8 Вт. Ascend 610 имеет чип вычислительную емкость до 160 топов и используется для автономного движения уровня 3 и 4 уровня. Процессор 610 имеет 64-битный четырехъядерный архитектуру процессора и продвинутая система 4G LTE, которая может сбалансировать энергопотребление и производительность высокопроизводительных смартфонов.
горизонт
Горизонт робототехника была основана в 2015 году для изготовления фишек AI для автономных транспортных средств и машин. Он также настроил программное обеспечение для этих чипов, которые могут быть установлены на таких устройствах, как автомобили и умные колонки. Robotics Horizon объявила о третьем автомобильном плане AI Travel 5 и в режиме реального времени в автомобильной операционной системе. Путешествие 5-х одно чипных вычислительных мощностей AI может достигать 128 топов. Целевые партнеры для дебюта путешествия 5 являются ведущими производителями оборудования, в том числе САИК, отличные стеновые моторы, Jianghuai Automobile, Ideal Motors, Changan Automobile и BYD.
Черный кунжут
Новый автономный микросхемы интеллектуальной технологии Black Seesame A1000 Pro популярен с вычислением вычисления, находящихся популярным среди таких чипов, производимых местными компаниями. Согласно интеллектуальным технологиям Black SeSame, A1000 Pro основан на чипе A1000 Компании, которая была оптимизирована со стандартной вычислительной емкостью до 106 вершин и максимум 196 лучших в режиме ускорения. Интеллектуальные технологии Black Seesame сотрудничают с такими компаниями, как NIO, SAIC, BYD, Dongfeng Motor, FAW Group и Bosch для обеспечения решений для систем помощи усовершенствованных водителей L2 / L3 и систем автономных систем вождения.
Xin Chi Technology
Технология XIN CHI - это полупроводниковая компания, штаб-квартира в Китае, сосредоточенная на решении высокопроизводительных автомобильных регуляторных микросхемы. Чип V9T, запущенный в 2021 году, может проехать до 1 топов. В 2022 году технологии Xin Chi запустит автономный водительский чип V9P / U, который имеет вычислительную мощность от 10 до 200 топов. Продукт имеет более высокую степень интеграции вычислительной мощности и может поддерживать автономное вождение уровня 3. В 2023 году технологии Xin Chi запустит чип автопилот V9S с более высокими вычислениями. Чип был разработан для архитектуры центральной вычислительной платформы. Вычислительная мощность составляет до 500-1000 топов, которые могут поддерживать автономные такси на уровне 4 или уровень автономной вождения уровня. В настоящее время V9 Xin Chi Technology (автоматическое вождение) принимает процесс 16 нм. Этот уровень технологии упал в области бытовой электроники, но в автомобильной промышленности 16 нм технологии по-прежнему является основной тенденцией.
Tesla.
Полностью автономный водительский чип (FSD-чип, ранее автопилот оборудования 3.0) - это автономный водительский чип, разработанный Tesla и запущен в начале 2019 года для использования в внутренних автомобилях компании. Тесла утверждает, что целью чипа является уровнем 4 и уровнем 5 автономное вождение. Он изготовлен с использованием технологии Samsung в 14 нм технологии. Чип FSD включает в себя 3 четырехъядерные кластеры Cortex-A72, в общей сложности 12 процессоров, работающие на 2,2 ГГц, MALI G71 MP12 GPU, работающие на 1 ГГц, две нервные блоки обработки, работающие в 2 ГГц, а также различные другие аппаратные ускорители Отказ
Автомобили Tesla самостоятельно управляются компьютером на основе двух новых чипов AI, каждый с ускорителем CPU, GPU и глубоким обучением. Компьютер имеет вычислительную мощность до 144 топов, позволяющих собирать данные из ряда камер объемных камер, радиолокационных, ультразвуковых и мощных алгоритмов глубоких нейронных сетевых сетей.
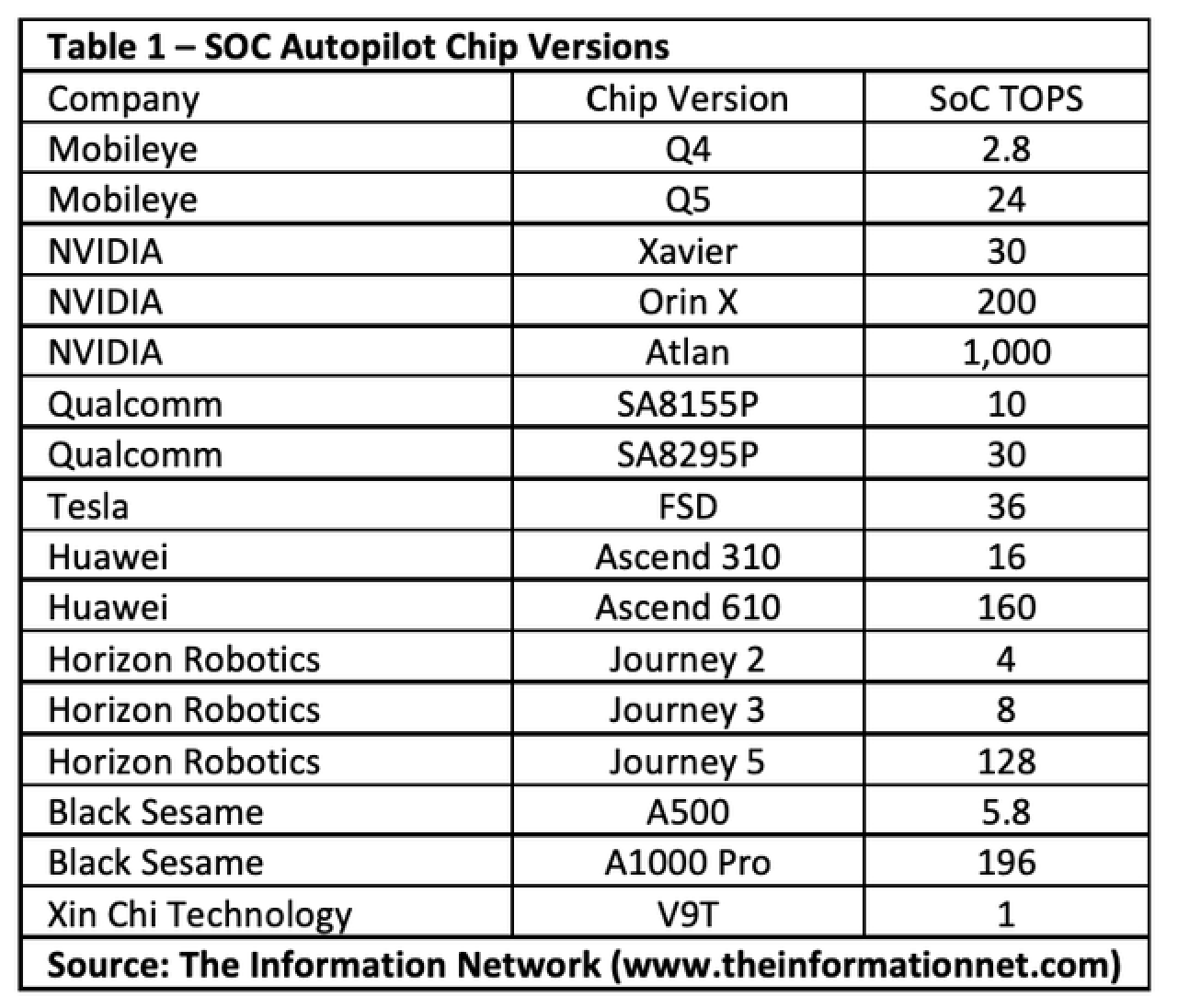
В следующей таблице отображаются версии чиповых версий (текущие и запланированные версии) этих компаний, а также вершины чипов. Согласно нашему докладу под названием «Горячие интегральные схемы: Искусственный интеллект (« АИ ») Анализ рынка, 5G, датчики изображения CMOS и чипсы памяти», вычислительная мощность чипов NVIDIA Orin может достигать 200 топов, что в 9 раз больше, чем Eyeq5. Оба путешествия 5 горизонта робота и Ascend 610 Huawei превышают EyeQ5 в вычислительной мощности.
Согласно данным Intel, ежегодный доход Summerye в 2020 году составил 967 млн. Долларов США, а в 2019 году было 879 миллионов долларов США, увеличившись на 10% в годовом исчислении. Компания рассчитывает достичь рекордных годовых доходов в этом году, что, как ожидается, будет более чем на 40% выше 2020 года. В 2020 году до 2020 года поставки CHAMET CHAMET CHADQ составили 19,3 миллиона по сравнению с 2,7 миллионами в 2014 году, представляя собой составную годовую скорость роста 39 %
В то время как Mobileye привлекла многие клиенты, Qualcomm объявила о своем сотрудничестве с BMW на 2021 инвесторовской конференции. Новые автомобили BMW будут использовать Snapdragon Snapdragon Snapdragon Snapdragon (включая чипсы) от 2025.
В дополнение к разрыву производительности обсуждается позже в этой статье, чип Intel's 3940 относится к серии E3900, которая была выпущена в 2016 году, используя процесс 14nm. Сначала он был в основном использован для чипов потребительских классов, а затем он был отдельно классифицирован как чипсы автомобильных классов. Компания CAR-класса - это серия A3900, а стоимость составляет около 40 долларов США. S8155 Qualcomm MakeComm - это высококачественный микросхемы, который стоит около 100 долларов.
Большинство самостоятельно-транспортных средств используют системы с камерами, радарами, лазерными датчиками и другими техническими системами для оценки дорожных условий и корректировки поведения вождения. Эти автомобили могут иметь адаптивный круиз-контроль, регулировку полосы движения полос и автоматическое торможение, рулевое управление и системы ускорения.
Уровень автономного вождения неотделимо от вычислительной мощности чипа. Автономная водительская промышленность, как правило, считает, что мощность вычислительной мощности чипа, необходимая для уровня 2 (триллион операций в секунду, «топы»), составляет менее 10 верхов, уровень 3 требует от 30 до 60 топов, а уровень 4 требует 100. Топы или выше, уровень 5 требует 1000 топов или выше. Именно из-за этого, что чип вычислительная мощность стала основной силой конкуренции между различными чипами.
Если автомобильная компания использует несколько чипов для настройки контроллера автономного вождения, они могут достигать 1024 топов, которые могут поддерживать автономное вождение уровня 4.
Хотя вычисляющие топы мощности одного чипа является ключевым индикатором, это не единственный индикатор. Автономное вождение - сложная система, которая требует совместной работы облака автомобильного дороги. Следовательно, в конкурсе чипов автопилота, в дополнение к ядру, существует также сотрудничество программного и аппаратного обеспечения, а также платформа и цепочка инструментов.
В настоящее время на автомобильном рынке Chip Ai Compints, которые негативно затронули Intel и Mobileye, включая Qualcomm и NVIDIA, TESLA и китайскую компанию Huawei, Horizon, Black Seaname и Technology Chi Chi.
Seekingalpha также перечислена подробная информация о продуктах и планах конкурентов Mobileye.
Qualcomm
Серия Intel A3900 основана на дизайне архитектуры x86 и была выпущена в 2016 году, используя процесс 14nm. Сначала он был в основном использован для чипов потребительских классов, а затем он был отдельно классифицирован как чипсы автомобильных классов. Компания CAR-класса - это серия A3900, а стоимость составляет около 40 долларов США. Обновленная версия EyeQ4, EyeQ5, будет выпущена в 2020 году. EyeQ5 был установлен только на модели Geely 001 Geely 001 в течение первого четвертого квартала этого года. EyeQ5 принимает 7nm Finfet Process, CHIP вычисление мощности составляет 24 верхних вершины.
SA8155P - это интегрированная платформа Cakpit встроенная кабина следующего поколения. Это чип уровня системы 7nM, разработанный с пользовательскими аппаратными модулями, включая восьмидерную подсистему CPU, и принимает CPU Qury Chare CROO, на основе архитектуры ARMV8. Чип уровня системы использует эффективную архитектуру машины, потребляемая мощность составляет менее 7 Вт, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 10 топов.
Платформа Snapdragon Snapdragon Qualcomm MakeComm MatoComm SA8295P использует 5 нм технологию технологии, с пропускной способностью чипов до 30 топов.
SA8155P - это интегрированная платформа Cakpit встроенная кабина следующего поколения. Это чип уровня системы 7nM, разработанный с пользовательскими аппаратными модулями, включая восьмидерную подсистему CPU, и принимает CPU Qury Chare CROO, на основе архитектуры ARMV8. Чип уровня системы использует эффективную архитектуру машины, потребляемая мощность составляет менее 7 Вт, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 10 топов. Платформа Snapdragon Snapdragon Qualcomm MakeComm MatoComm SA8295P использует 5 нм технологию технологии, с пропускной способностью чипов до 30 топов.
NVIDIA
Процессор Xavier имеет программируемый ускоритель CPU, GPU и глубокого обучения, а вычислительная емкость чипов может достигать 30 топов. NVIDIA's Next-Generation Autopilot Chip Chip Chip также начнет массовое производство в 2022 году. Одной вычислительной мощности чипа Orin составляет 254 топов, что в 10 раз выше, чем вычислительная мощность EyeQ5. Вычислительная мощность NVIDIA ATLAN на вычислительной емкости NVIDIA может достигать 1000 топов (ожидается, что оно обеспечивает образцы разработчикам в 2023 году).
Huawei
Huawei позиционирует его как поставщик уровня 1 и построить «автомобильную экосистему 5G» с целью высококачественного автономного рынка вождения, который нельзя игнорировать.
Вычислительная мощность чипа Huawei Ascend 310 может достигать 16 топов, а потребляемая мощность составляет всего 8 Вт. Ascend 610 имеет чип вычислительную емкость до 160 топов и используется для автономного движения уровня 3 и 4 уровня. Процессор 610 имеет 64-битный четырехъядерный архитектуру процессора и продвинутая система 4G LTE, которая может сбалансировать энергопотребление и производительность высокопроизводительных смартфонов.
горизонт
Горизонт робототехника была основана в 2015 году для изготовления фишек AI для автономных транспортных средств и машин. Он также настроил программное обеспечение для этих чипов, которые могут быть установлены на таких устройствах, как автомобили и умные колонки. Robotics Horizon объявила о третьем автомобильном плане AI Travel 5 и в режиме реального времени в автомобильной операционной системе. Путешествие 5-х одно чипных вычислительных мощностей AI может достигать 128 топов. Целевые партнеры для дебюта путешествия 5 являются ведущими производителями оборудования, в том числе САИК, отличные стеновые моторы, Jianghuai Automobile, Ideal Motors, Changan Automobile и BYD.
Черный кунжут
Новый автономный микросхемы интеллектуальной технологии Black Seesame A1000 Pro популярен с вычислением вычисления, находящихся популярным среди таких чипов, производимых местными компаниями. Согласно интеллектуальным технологиям Black SeSame, A1000 Pro основан на чипе A1000 Компании, которая была оптимизирована со стандартной вычислительной емкостью до 106 вершин и максимум 196 лучших в режиме ускорения. Интеллектуальные технологии Black Seesame сотрудничают с такими компаниями, как NIO, SAIC, BYD, Dongfeng Motor, FAW Group и Bosch для обеспечения решений для систем помощи усовершенствованных водителей L2 / L3 и систем автономных систем вождения.
Xin Chi Technology
Технология XIN CHI - это полупроводниковая компания, штаб-квартира в Китае, сосредоточенная на решении высокопроизводительных автомобильных регуляторных микросхемы. Чип V9T, запущенный в 2021 году, может проехать до 1 топов. В 2022 году технологии Xin Chi запустит автономный водительский чип V9P / U, который имеет вычислительную мощность от 10 до 200 топов. Продукт имеет более высокую степень интеграции вычислительной мощности и может поддерживать автономное вождение уровня 3. В 2023 году технологии Xin Chi запустит чип автопилот V9S с более высокими вычислениями. Чип был разработан для архитектуры центральной вычислительной платформы. Вычислительная мощность составляет до 500-1000 топов, которые могут поддерживать автономные такси на уровне 4 или уровень автономной вождения уровня. В настоящее время V9 Xin Chi Technology (автоматическое вождение) принимает процесс 16 нм. Этот уровень технологии упал в области бытовой электроники, но в автомобильной промышленности 16 нм технологии по-прежнему является основной тенденцией.
Tesla.
Полностью автономный водительский чип (FSD-чип, ранее автопилот оборудования 3.0) - это автономный водительский чип, разработанный Tesla и запущен в начале 2019 года для использования в внутренних автомобилях компании. Тесла утверждает, что целью чипа является уровнем 4 и уровнем 5 автономное вождение. Он изготовлен с использованием технологии Samsung в 14 нм технологии. Чип FSD включает в себя 3 четырехъядерные кластеры Cortex-A72, в общей сложности 12 процессоров, работающие на 2,2 ГГц, MALI G71 MP12 GPU, работающие на 1 ГГц, две нервные блоки обработки, работающие в 2 ГГц, а также различные другие аппаратные ускорители Отказ
Автомобили Tesla самостоятельно управляются компьютером на основе двух новых чипов AI, каждый с ускорителем CPU, GPU и глубоким обучением. Компьютер имеет вычислительную мощность до 144 топов, позволяющих собирать данные из ряда камер объемных камер, радиолокационных, ультразвуковых и мощных алгоритмов глубоких нейронных сетевых сетей.
В следующей таблице отображаются версии чиповых версий (текущие и запланированные версии) этих компаний, а также вершины чипов. Согласно нашему докладу под названием «Горячие интегральные схемы: Искусственный интеллект (« АИ ») Анализ рынка, 5G, датчики изображения CMOS и чипсы памяти», вычислительная мощность чипов NVIDIA Orin может достигать 200 топов, что в 9 раз больше, чем Eyeq5. Оба путешествия 5 горизонта робота и Ascend 610 Huawei превышают EyeQ5 в вычислительной мощности.
ADAS определяется одним из следующих шести характерных уровней (L0-L5):
В 2020 году уровень проникновения на уровне 2-го автономного вождения в Китае достигнет 15%. Это означает, что почти 4 миллиона новых автомобилей оснащены автопилотами уровня 2. Предполагается, что к 2030 году автомобили самостоятельно приходится более 40% от общего объема пробега, а уровень проникновения полностью автоматических новых автомобилей достигнет 10%.
Уолл-стрит прогнозирует, что с 2019 по 2030 год уровень проникновения китайского самообладающего бренда пассажирских автомобилей от ADAS до уровня 3 увеличится с 20% до 75%. Это означает, что размер рынка чипов увеличится с 50 миллионов долларов США до более чем 1,5 миллиарда долларов США. Китайские автомобили меньше страдают от «нехватки» полупроводников. Аналогичным образом, китайские независимые бренды также будут использовать автомобильные чипсы на дому.
Сильный спрос на китайском рынке имеет решающее значение для Mobileye и его конкурентов, потому что Huawei и Chinalling Start-Ups ослабят лидерство на рынке Mobileye. Таким образом, робототехника China Horizon сотрудничает с ведущими производителями оборудования, включая SAIC, Great Wall Motors, Jianghuai Automobile, Ideal Motors, Changan Automobile и BYD - оригинальные производители оборудования в Китае.
SAIC - это не только инвестор в робототехнике горизонта, но и инвестор в черных сезате технологии. В августе 2020 года SAIC заявил, что в инвестировании он инвестировал более десятка ведущих отечественных чиповых компаний, включая горизонт робототехника и черную сезамную технологию.
С глобальной точки зрения, к 2025 году только 15% автомобилей в мире не будет иметь ADAS систему автоматического вождения, а в 2020 году эта доля будет 42%, а 40% автомобилей будет оснащен системой автоматического вождения 1-го уровня. Важно отметить, что к 2025 году 36% транспортных средств будут оборудованы L2 автономной вождения системы, увеличение с 10% в 2020 году только 9% автомобилей имеют автономные системы вождения с 3-го уровня или выше функций. Intel объявила 7 декабря 2021 года о том, что компания планирует публично СПИСКА Mobileye в самостоятельном вождении автомобилей. Откровенно говоря, это не «пресловутый» момент для Intel.
Автономная технология вождения все еще находится в зачаточном этапе развития, и далеко от достижения зрелой стадии. Это делает автомобильный автопилот рынка чипа жесткой конкуренции, и Mobileye налаживает партнерские отношения с автомобильными компаниями на протяжении многих лет. чип уровня системы поставки Mobileye были 19,3 млн долларов, а чип поставка Horizon была почти 500 тысяч.
Реальная разница заключается в вычислительной мощности. Несмотря на то, вычислительная мощность Mobileye составляет всего 24 ТОПС, путешествие 5 чип Horizon Робот имеет 128 TOPS. Чип вычислительной мощности, необходимой для уровня 2 автономного вождения составляет менее 10 вершин, уровень 3 автономное вождение требует от 30 до 60 TOPS, а уровень 4 требует более 100 вершин. Это означает, что горизонт робот, установленный в 2015 году и Mobileye создана в 1999 году может достичь уровня 4 автономного вождения, в то время как Mobileye останавливается на уровень 2 автономного вождение.
Mobileye и самостоятельного вождения автомобилей не являются стратегическим направлением набор генеральный директор Гелсинджера для Intel. Позднее он идет общественность, тем больше сопротивление, которое Mobileye столкнется, и он также обеспокоен низкой оценкой IPO.
Это разделение является важным решением, принятым Intel, поскольку Intel занимается чип бизнеса, компания будет использовать средства IPO, чтобы создать новую ФАБ. Кроме того, STMicroelectronics разрабатывает чипы EyeQ и TSMC производит чипы EyeQ. В последние годы доля процессор Intel проиграл AMD и упал в низкий период. В любом случае, это не повлияет на цели Intel по избавлению от низкого периода.
В 2020 году уровень проникновения на уровне 2-го автономного вождения в Китае достигнет 15%. Это означает, что почти 4 миллиона новых автомобилей оснащены автопилотами уровня 2. Предполагается, что к 2030 году автомобили самостоятельно приходится более 40% от общего объема пробега, а уровень проникновения полностью автоматических новых автомобилей достигнет 10%.
Уолл-стрит прогнозирует, что с 2019 по 2030 год уровень проникновения китайского самообладающего бренда пассажирских автомобилей от ADAS до уровня 3 увеличится с 20% до 75%. Это означает, что размер рынка чипов увеличится с 50 миллионов долларов США до более чем 1,5 миллиарда долларов США. Китайские автомобили меньше страдают от «нехватки» полупроводников. Аналогичным образом, китайские независимые бренды также будут использовать автомобильные чипсы на дому.
Сильный спрос на китайском рынке имеет решающее значение для Mobileye и его конкурентов, потому что Huawei и Chinalling Start-Ups ослабят лидерство на рынке Mobileye. Таким образом, робототехника China Horizon сотрудничает с ведущими производителями оборудования, включая SAIC, Great Wall Motors, Jianghuai Automobile, Ideal Motors, Changan Automobile и BYD - оригинальные производители оборудования в Китае.
SAIC - это не только инвестор в робототехнике горизонта, но и инвестор в черных сезате технологии. В августе 2020 года SAIC заявил, что в инвестировании он инвестировал более десятка ведущих отечественных чиповых компаний, включая горизонт робототехника и черную сезамную технологию.
С глобальной точки зрения, к 2025 году только 15% автомобилей в мире не будет иметь ADAS систему автоматического вождения, а в 2020 году эта доля будет 42%, а 40% автомобилей будет оснащен системой автоматического вождения 1-го уровня. Важно отметить, что к 2025 году 36% транспортных средств будут оборудованы L2 автономной вождения системы, увеличение с 10% в 2020 году только 9% автомобилей имеют автономные системы вождения с 3-го уровня или выше функций. Intel объявила 7 декабря 2021 года о том, что компания планирует публично СПИСКА Mobileye в самостоятельном вождении автомобилей. Откровенно говоря, это не «пресловутый» момент для Intel.
Автономная технология вождения все еще находится в зачаточном этапе развития, и далеко от достижения зрелой стадии. Это делает автомобильный автопилот рынка чипа жесткой конкуренции, и Mobileye налаживает партнерские отношения с автомобильными компаниями на протяжении многих лет. чип уровня системы поставки Mobileye были 19,3 млн долларов, а чип поставка Horizon была почти 500 тысяч.
Реальная разница заключается в вычислительной мощности. Несмотря на то, вычислительная мощность Mobileye составляет всего 24 ТОПС, путешествие 5 чип Horizon Робот имеет 128 TOPS. Чип вычислительной мощности, необходимой для уровня 2 автономного вождения составляет менее 10 вершин, уровень 3 автономное вождение требует от 30 до 60 TOPS, а уровень 4 требует более 100 вершин. Это означает, что горизонт робот, установленный в 2015 году и Mobileye создана в 1999 году может достичь уровня 4 автономного вождения, в то время как Mobileye останавливается на уровень 2 автономного вождение.
Mobileye и самостоятельного вождения автомобилей не являются стратегическим направлением набор генеральный директор Гелсинджера для Intel. Позднее он идет общественность, тем больше сопротивление, которое Mobileye столкнется, и он также обеспокоен низкой оценкой IPO.
Это разделение является важным решением, принятым Intel, поскольку Intel занимается чип бизнеса, компания будет использовать средства IPO, чтобы создать новую ФАБ. Кроме того, STMicroelectronics разрабатывает чипы EyeQ и TSMC производит чипы EyeQ. В последние годы доля процессор Intel проиграл AMD и упал в низкий период. В любом случае, это не повлияет на цели Intel по избавлению от низкого периода.
